2025
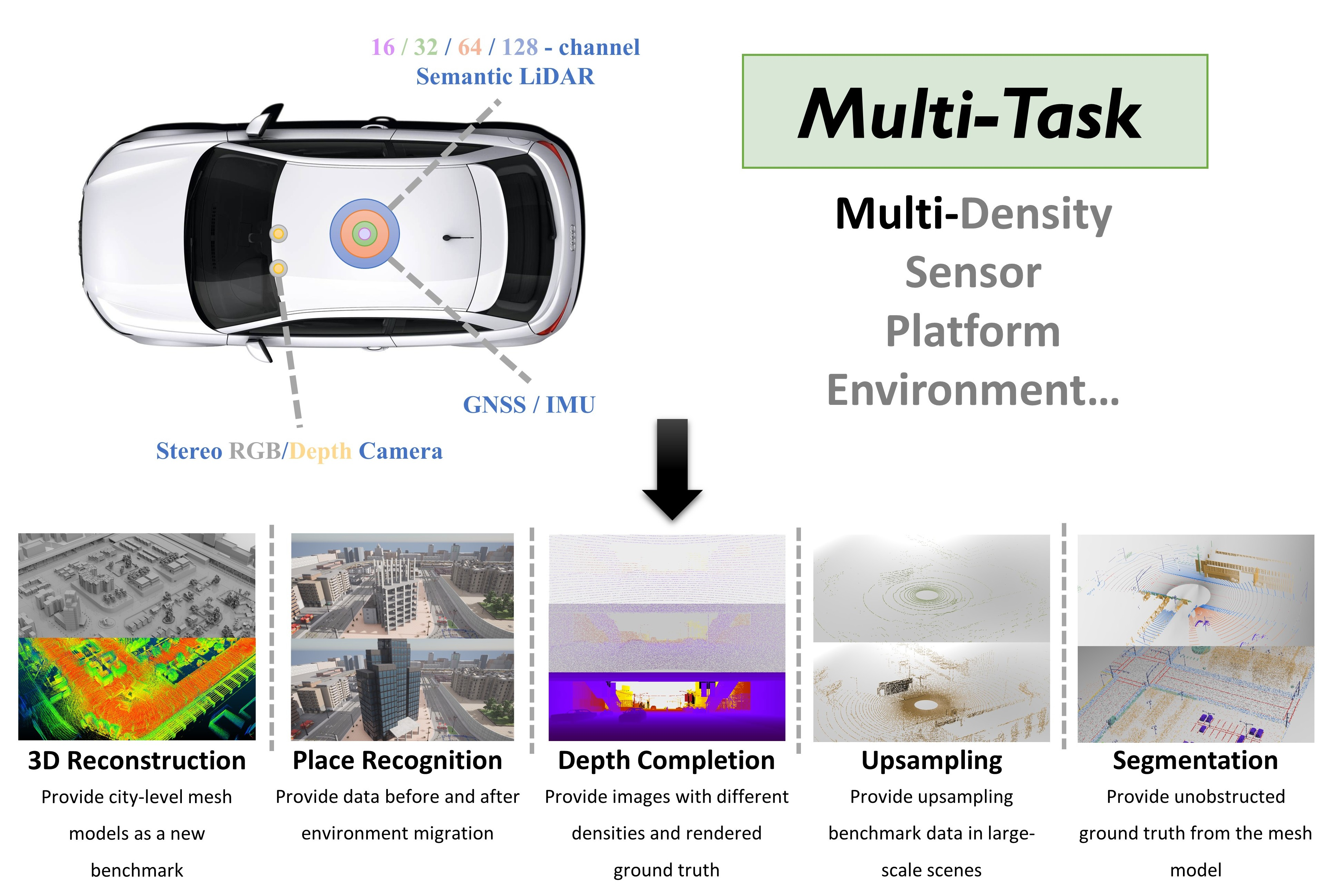
WHU-Synthetic: A Synthetic Perception Dataset for 3D Multi-task Model Research
Jiahao Zhou*, Chen Long*, Yue Xie, Jialiang Wang, Conglang Zhang, Boheng Li, Haiping Wang, Zhe Chen†, Zhen Dong
Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (IF: 7.5) 2025
We introduce WHU-Synthetic, a large-scale 3D synthetic perception dataset designed for multi-task learning, from the initial data augmentation, through scene understanding , to macro-level tasks. Besides, we implement several novel settings, making it possible to realize certain ideas that are difficult to achieve in real-world scenarios, such as sampling on city-level models, providing point clouds with different densities, and simulating temporal changes.

2024
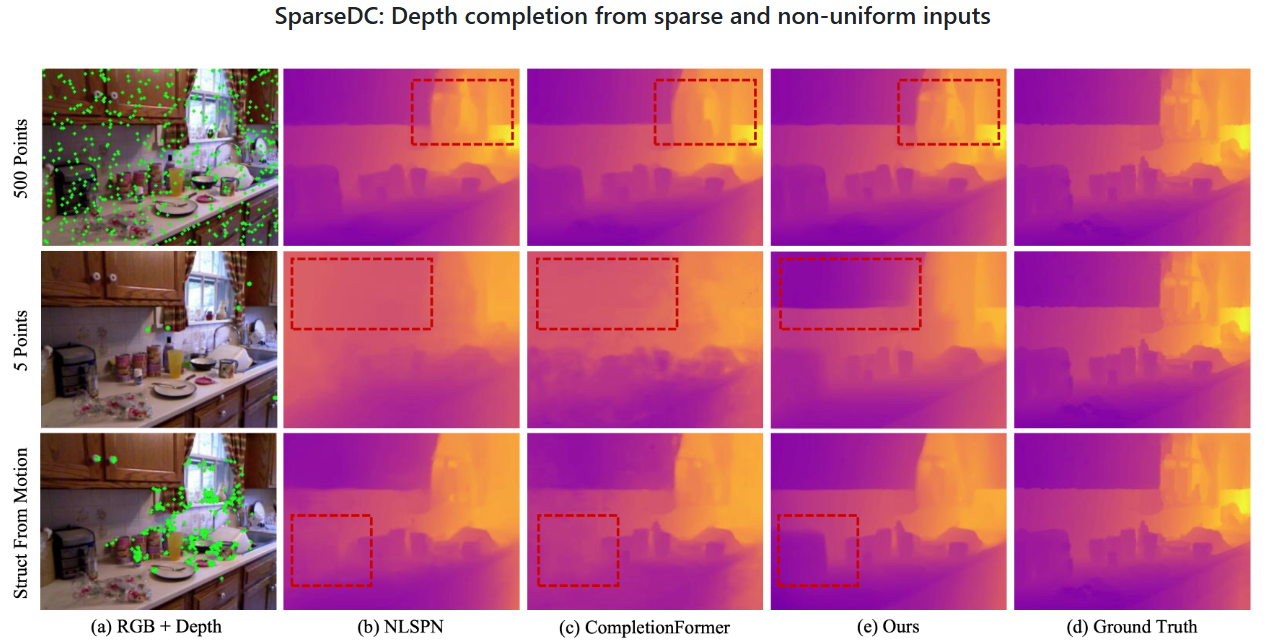
SparseDC: Depth Completion From Sparse and Non-uniform Inputs
Chen Long*, Wenxiao Zhang*, Zhe Chen, Haiping Wang, Yuan Liu, Zhen Cao, Zhen Dong†, Bisheng Yang
Information Fusion (IF: 14.8) 2024
SparseDC is a model for Depth Completion from Sparse and non-uniform inputs. Numerous experiments conducted both indoors and outdoors show how robust and effective the framework is when facing sparse and non-uniform input depths.

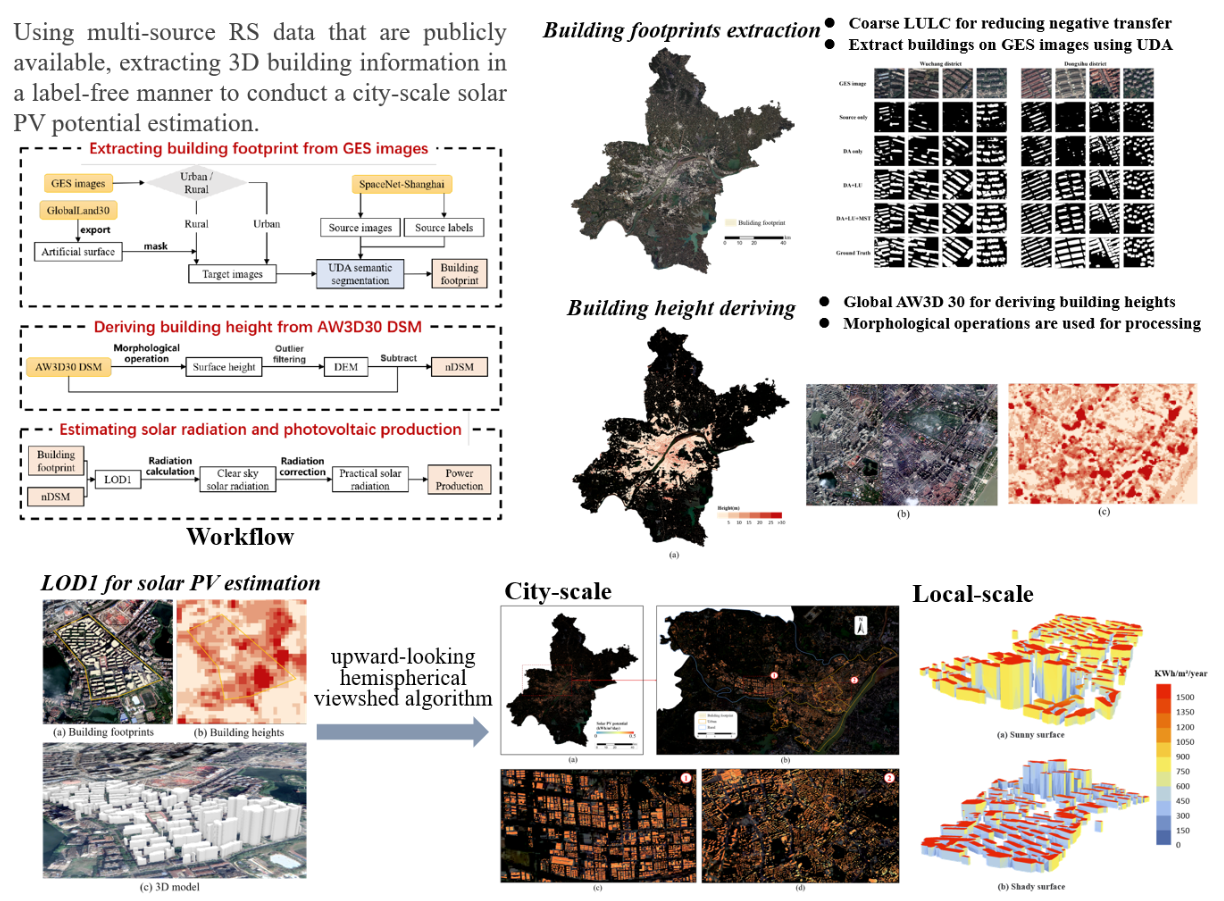
City-scale solar PV potential estimation on 3D buildings using multi-source RS data: A case study in Wuhan, China
Zhe Chen, Bisheng Yang†, Rui Zhu, Zhen Dong
Applied Energy (IF: 10.1) 2024
This study proposes a framework for estimating the solar PV potential of city-level building surfaces without human annotation and data acquisition costs. Buildings are extracted from Google satellite images through multi-space joint optimization domain adaptation network, and LoD1 models are generated by combining global DSM with building footprints. The framework was verified by taking Wuhan city as an example.

2022
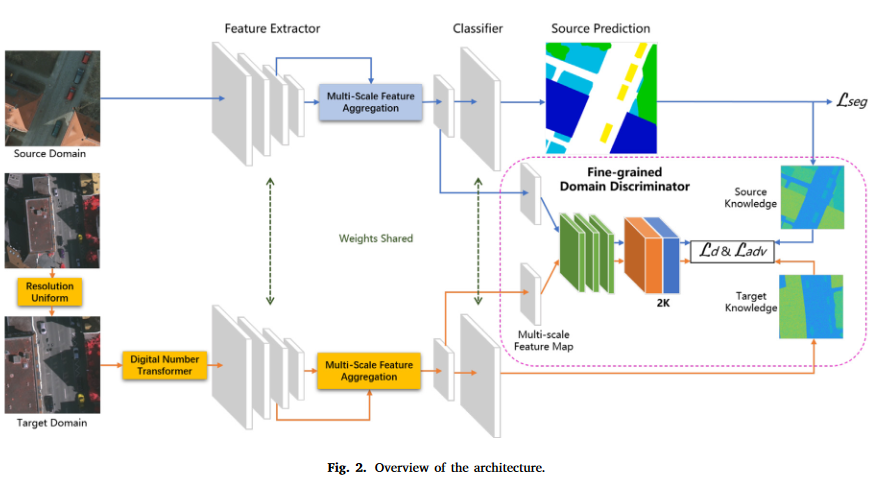
Joint alignment of the distribution in input and feature space for cross-domain aerial image semantic segmentation
Zhe Chen, Bisheng Yang, Ailong Ma, Mingjun Peng, Haiting Li, Tao Chen, Chi Chen†, Zhen Dong
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation (IF: 7.6) 2022
A framework to jointly align the distribution in input and feature space for cross-domain aerial image semantic segmentation, our method demonstrates excellent performance in various cross-domain scenarios, including the discrepancy in geographic position and the discrepancy in both geographic position and imaging mode.
